ZURNAI (NALMEFENE INJECTION) works fast1
At 5 minutes, mean change in minute ventilation (MV) from nadir* was 4.42 L/min
*MV nadir was defined as a 50% reduction in MV from baseline or the MV reduction achieved following the maximum permitted fentanyl titration.
Pharmacodynamic study assessed the ability of ZURNAI to reverse respiratory depression1
An experimental clinical opioid-induced respiratory depression (OIRD) model assessed pharmacodynamic effects of ZURNAI, specifically changes in minute ventilation (MV) during administration of a 3-step intravenous fentanyl infusion.
Participants: 24 healthy adult subjects who were opioid-experienced and non-opioid dependent.
NAL1004 study design
Fentanyl was infused until MV nadir* (functional OIRD) was achieved
Following attainment of MV nadir, fentanyl infusion rate was decreased to maintain the fentanyl concentrations
ZURNAI was administered at 10 minutes following MV nadir
10 minutes following ZURNAI administration, fentanyl infusion rate was further decreased to maintain constant fentanyl concentrations for remaining duration of reversal session
*MV nadir was defined as a 50% reduction in MV from baseline or the MV reduction achieved following the maximum permitted fentanyl titration.
*MV nadir was defined as a 50% reduction in MV from baseline or the MV reduction achieved following the maximum permitted fentanyl titration.
This study was conducted in an experimental setting where fentanyl was infused over an extended period and titrated to maintain consistent plasma concentrations. As such, the clinical implications of these findings for real-world overdose situations are unknown.1
Reversal of fentanyl-induced respiratory depression in adult healthy volunteers treated with ZURNAI1
Percent recovery of respiratory drive after fentanyl infusion in minute ventilation (mean SD) in adult healthy volunteers with ZURNAI 1.5 mg1
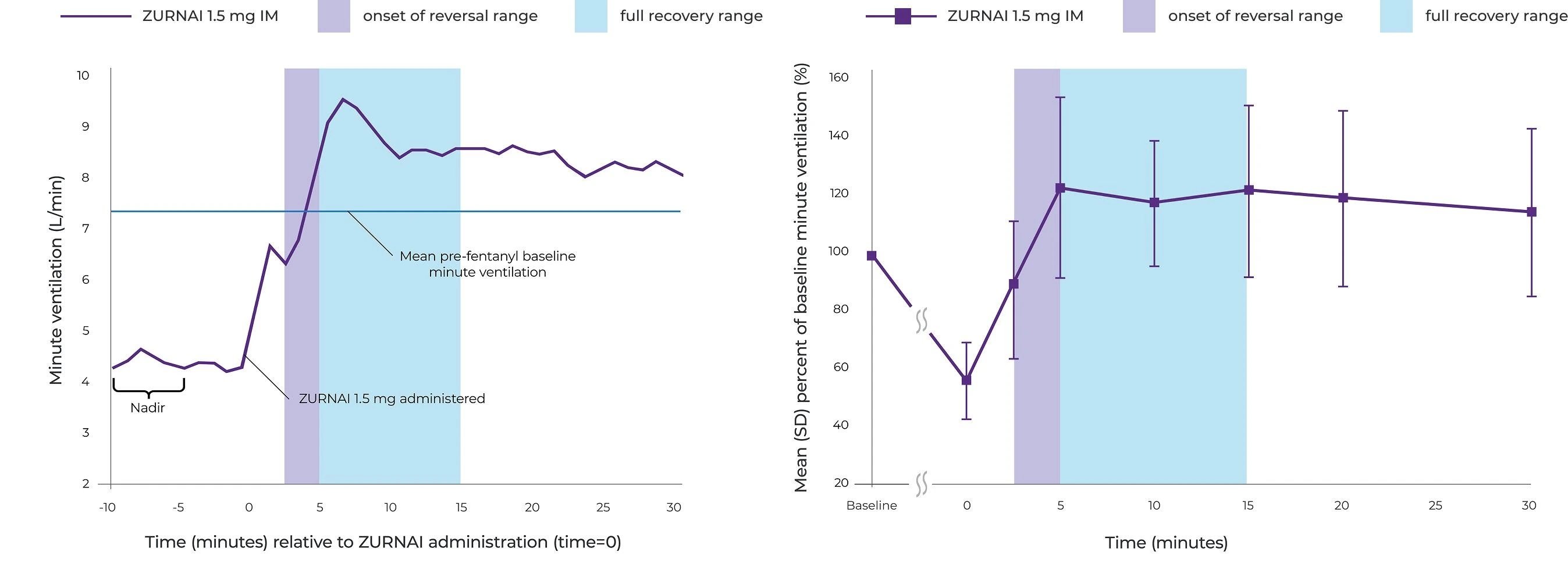
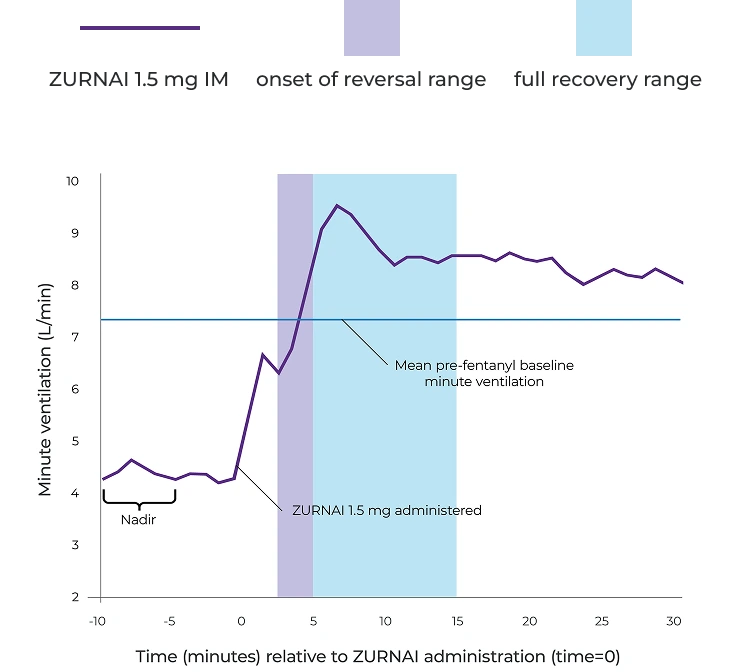
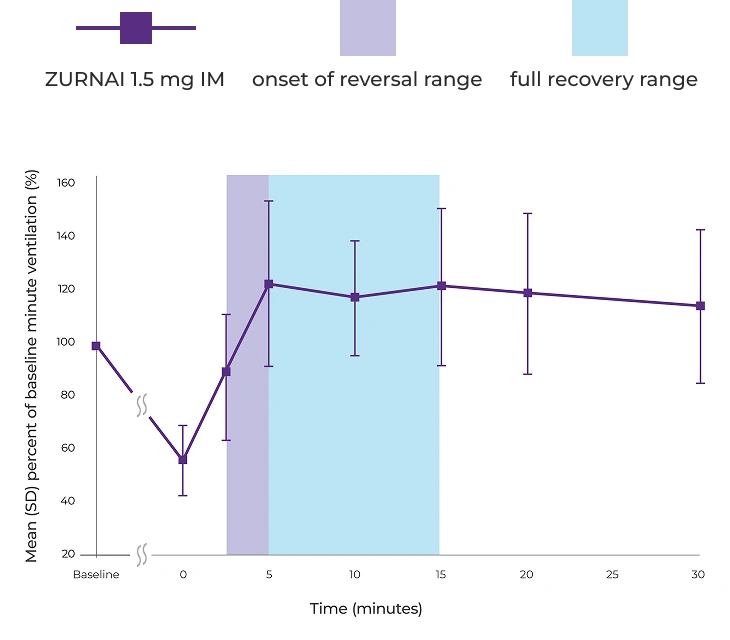
IM=intramuscular; SD=standard deviation.
ZURNAI has a long half-life1‡
Pharmacokinetic (PK) Study NAL10051
To determine the relative bioavailability of ZURNAI, one dose was administered intramuscularly (IM) in 24 healthy adult subjects. A 1.0 mg dose of nalmefene administered as an IM injection was used as a comparator.
While the duration of action of nalmefene is as long as most opioids,§ a recurrence of respiratory depression is possible, even after an apparently adequate initial response to ZURNAI treatment.
Therefore, it is necessary to seek emergency medical assistance immediately after administration of the first dose of ZURNAI and to keep the patient under continued surveillance. A second dose may be necessary if there is recurrence of symptoms of opioid overdose.
†Pharmacokinetic studies are conducted in healthy subjects; as such, the clinical implications of these findings for real-world overdose situations are unknown.
‡ZURNAI mean elimination half-life of 9.07 hours is based on a pharmacokinetic study of 24 healthy adult subjects given a single dose of intramuscular ZURNAI.1
§The half-life of fentanyl used as anesthesia has been shown to be about 7.5 hours; the half-life of illicit fentanyl has not been characterized.2
In the PK study NAL1005, the mean TERMINAL elimination half-life of ZURNAI was 9.07 hours1
Pharmacokinetic studies are conducted in healthy subjects; as such, the clinical implications of these findings for real-world overdose situations are unknown.
Key pharmacokinetic parameters in healthy volunteers (n=24)
Cmax=maximum concentration; IV=intravenous; Tmax=time to maximum concentration.
‖Presented as geometric mean (coefficient of variation percentage).
¶Presented as median (range).
#Presented as arithmetic mean (coefficient of variation percentage).
 Not actual size.
Not actual size.Clinically demonstrated safety profile1
The safety of ZURNAI is supported by a pharmacokinetic study of healthy adults under normal conditions and by a pharmacodynamic study evaluating the effects of ZURNAI under steady-state opioid infusion.1
ZURNAI: Important considerations
- ZURNAI is not a substitute for emergency care1
- Use ZURNAI with extreme caution in patients with known physical dependence on opioids, as acute withdrawal symptoms may occur1
- Any attempt to overcome receptor blockade from opioid antagonists such as ZURNAI with large doses of opioids may lead to opioid intoxication and death1
- Reversal of respiratory depression caused by partial agonists or mixed agonist/antagonists, such as buprenorphine and pentazocine, may be incomplete and may require repeated administration of ZURNAI using a new auto-injector1
Relative frequencies of most common adverse reactions that occurred in greater
than 5% of subjects in Study NAL1004 and Study NAL10051
| System organ class Adverse event | Pooled NAL1004 and NAL1005 N=44 n (%) |
|---|---|
| Any adverse reaction | 28 (63.6) |
| Nervous system disorders Dizziness Headache Allodynia Burning sensation | 7 (15.9) 8 (18.2) 5 (11.4) 3 (6.8) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders Nausea Vomiting | 8 (18.2) 5 (11.4) |
| Ear and labyrinth disorders Tinnitus Ear discomfort | 4 (9.1) 3 (6.8) |
| System organ class Adverse event | Pooled NAL1004 and NAL1005 N=44 n (%) |
|---|---|
| Cardiac disorders Palpitations | 4 (9.1) |
| General disorders and administration-site conditions Feeling hot Chills Feeling abnormal | 11 (25.0) 6 (13.6) 3 (6.8) |
| Vascular disorders Hot flush | 3 (6.8) |
| Psychiatric disorders Irritability | 3 (6.8) |
It is necessary to seek emergency medical assistance immediately after administration of the first dose of ZURNAI and to keep the patient under continued surveillance.1